The Critical Role of Accurate Labeling in Manufacturing
July 18, 2022
Proactive Strategies to Identify and Manage Workplace Hazards
July 18, 2022
The Critical Role of Accurate Labeling in Manufacturing
July 18, 2022
Proactive Strategies to Identify and Manage Workplace Hazards
July 18, 2022In industrial environments, implementing reliable lockout procedures is non-negotiable for maintaining safety during maintenance, installation, or repair work. Whether handling electrical, thermal, chemical, pneumatic, hydraulic, mechanical, or gravitational energy, securing equipment in a non-operational state is essential. This guide delves into key lockout systems, offering actionable insights to bolster safety and prevent accidents in manufacturing and industrial settings.
Lockout Cables: Versatility in Action
Lockout cables are a practical solution for equipment with multiple energy sources. They enable the simultaneous locking of several disconnect switches with a single cable, streamlining the lockout process. To maximize effectiveness, ensure the cable diameter prevents accidental activation of disconnects. Using a scissor lock adapter allows for the attachment of multiple locks, further enhancing safety measures.

Circuit Breaker Lockout: The Electrical Safety Backbone
Securing circuit breakers is critical for maintaining electrical safety. When working on a panel connected to a main breaker, locking the entire panel can effectively neutralize all power, creating a hazard-free workspace. This approach is particularly beneficial when no other personnel require panel access during the task.
Cord Locks: Managing Plugged-In Equipment
For equipment that remains plugged in, the visibility and accessibility of the plug dictate the lockout method. If the plug is within sight and reach, a lock may not be necessary. However, if it is out of view, securing the cord with an adapter and lock—or attaching it to an immovable object—can prevent accidental reconnection and ensure a safe working environment.
Lockout Boards: Streamlining Organization
Lockout stations or boards play a vital role in organizing safety procedures. These boards store keyed locks, tags, and other lockout devices, ensuring quick access to essential tools. A one-key-per-lock system ensures accountability, with keys promptly returned to the station upon task completion.
Key Box Systems: Coordinated Safety for Complex Machinery
For equipment powered by multiple energy sources, key box systems offer an efficient lockout method. A wall-mounted box with dual lock sets—each mastered to different keys—acts as the locked-out power source. These systems adhere to all lockout regulations and allow each worker to attach their personal lock, ensuring enhanced coordination and safety.
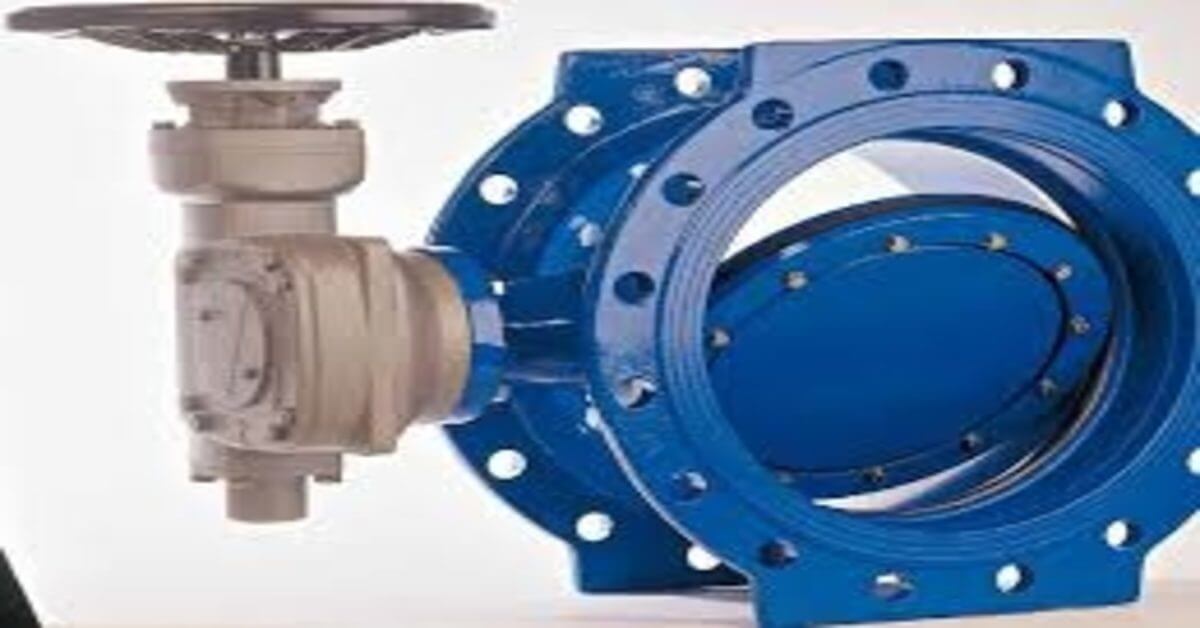
Valve Lockout: Securing Fluid Systems
Locking out valves is essential to prevent the unintended activation of fluid-powered equipment. A durable device is affixed over the valve’s operational component and secured with hasps or padlocks. For maximum safety, every worker involved in the task should attach their padlock and remove it only after completing their work.
By implementing these lockout systems—from versatile cables to specialized valve lockouts—industrial facilities can ensure both compliance and safety. A proactive approach to lockout procedures not only protects personnel but also upholds operational integrity. For expert solutions and premium safety products, partner with EZSecur. Visit www.ezsecur.com to learn more.